The 4 Pillars of Purchasing: Mastering Both Strategic Sourcing and Global Procurement

In today's volatile global economy, procurement and purchasing teams face unprecedented challenges. Supply chain disruptions, inflationary pressures, and the demand for ethical sourcing are constant concerns. Amid this complexity, a common question arises: What are the four pillars of purchasing?
The answer isn't singular. The term "four pillars" refers to two powerful, complementary frameworks that form the bedrock of a world-class procurement function:
The Four Pillars of Strategic Sourcing:Focused on optimizing the core process of how you buy.
The Four Pillars of Global Procurement: Focused on managing the operational complexity of buying across international borders.
This comprehensive guide will demystify both sets of pillars, explaining their components, importance, and—crucially—how to implement them to build a resilient, efficient, and strategic purchasing operation.
Strategic sourcing is the deliberate, data-driven process of developing supply channels at the lowest total cost, not just the lowest price. Its four pillars create a continuous cycle of improvement.
What it is:Spend analysis is the systematic process of collecting, cleansing, classifying, and analyzing all of an organization's expenditure data. It's about transforming raw, messy data into a clear map of where money is going.
Why It Matters: You cannot manage what you cannot measure. Spend visibility is the absolute prerequisite for any strategic decision. It uncovers hidden savings opportunities, reveals maverick spending, and identifies leverageable spend categories.
How to Implement & Get Started:
Data Aggregation: Pull data from all sources—ERPs, AP systems, and card programs.
Cleansing & Standardization: Correct errors and standardize vendor names (e.g., "IBM," "Int'l Business Machines," and "IBM Inc." become one).
Classification: Categorize spending using a system like UNSPSC or a custom taxonomy.
Analysis & Reporting: Identify trends, top suppliers, and opportunities for consolidation.
Long-tail KWs covered:
What it is: This is the core process of identifying, evaluating, and selecting suppliers based on the insights from spend analysis. It moves beyond transactional purchasing to focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
Why It Matters:Effective sourcing ensures you get the best value—a combination of cost, quality, service, innovation, and risk mitigation. It’s about building a competitive advantage through your supply base.
How to Implement & Get Started:
Market Research: Understand the supplier landscape and market dynamics.
Develop Sourcing Strategy: Decide on single vs. multi-sourcing, global vs. local.
RFx Process: Use Requests for Information (RFI), Proposals (RFP), and Quotations (RFQ) to gather comparable data.
Supplier Evaluation & Negotiation: Score suppliers objectively and negotiate terms.
Long-tail KWs covered:
What it is:Contract management is the process of creating, executing, and managing the agreements that formalize supplier relationships. It ensures the value captured during negotiation is realized.
Why It Matters:A handshake isn't enough. Strong contracts mitigate risk, ensure compliance, define performance metrics (SLAs/KPIs), and provide a legal framework for resolving disputes.
How to Implement & Get Started:
Centralized Repository: Store all contracts in a single, accessible location.
Key Clause Management: Standardize important terms like liability, termination, and SLA penalties.
Obligation Management: Track milestones, deliverables, and renewals proactively.
Compliance Monitoring: Ensure both parties are adhering to the agreed terms.
Long-tail KWs covered:
What it is: SRM is the proactive, strategic management of interactions with key suppliers. It’s about moving from a transactional, adversarial relationship to a collaborative partnership.
Why It Matters: Your critical suppliers are extensions of your enterprise. Strong relationships lead to innovation, preferential treatment during shortages, continuous improvement, and shared risk management.

How to Implement & Get Started:
Supplier Segmentation: Classify suppliers based on risk and criticality (e.g., strategic, bottleneck, leverage, routine).
Performance Management: Regularly review KPIs like on-time delivery, quality rates, and innovation ideas.
Joint Business Reviews: Hold quarterly or annual meetings to review performance, share strategy, and solve problems.
Development & Collaboration: Co-develop new products or processes with strategic partners.
Long-tail KWs covered:
When your sourcing activities cross borders, a new layer of complexity is added. These four pillars are critical for managing that complexity.
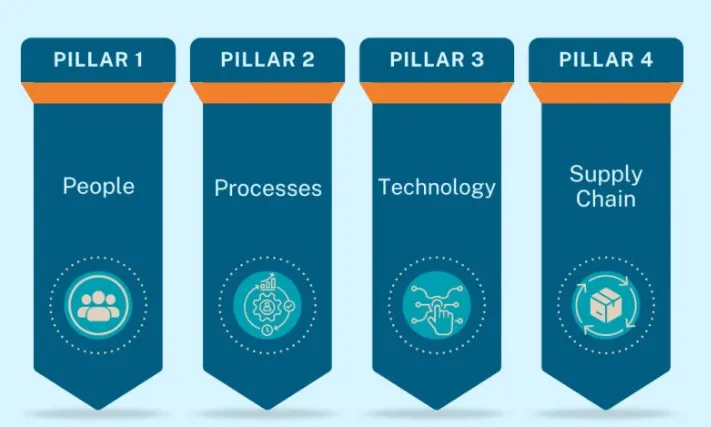
What it is: This refers to the talent, skills, and culture of your procurement team and its extended network. It includes internal staff, external partners, and leadership.
Why it Matters: The best processes and technology are useless without the right people to run them. Global procurement requires expertise in international trade, cross-cultural negotiation, risk mitigation, and local regulations.
How to Implement & Get Started: Invest in continuous training, hire for diversity of thought and experience, and consider leveraging third-party global procurement services with on-the-ground expertise.
What it is: These are the standardized, yet flexible, workflows that govern global procurement activities—from requisition to payment—across different regions and business units.
Why it Matters: Standardization ensures consistency, control, efficiency, and compliance. It prevents chaos and allows for scalability across diverse operating environments.
How to Implement & Get Started: Document and map core processes, implement global procurement policies (with allowable local variations), and automate workflows to reduce errors and delays.
What it is: The suite of digital tools that enable global procurement, including ERP modules, Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) software, spend analytics platforms, and digital procurement catalogs.
Why it Matters: Technology provides the global spend visibility needed for decision-making. It automates processes, manages multi-currency and multi-language requirements, and provides data-driven insights.
How to Implement & Get Started: Evaluate integrated procurement suites, prioritize cloud-based solutions for accessibility, and ensure robust data analytics and reporting capabilities are core features.
What it is: The active management of the entire flow of goods, information, and finances from your supplier's supplier to your customer. It encompasses logistics, inventory management, and risk mitigation.
Why it Matters: Global supply chains are inherently fragile. Managing this pillar directly impacts cost, reliability, and resilience. Disruptions in one part of the world can halt production in another.
How to Implement & Get Started: Conduct thorough supply chain mapping, diversify your supplier base geographically, develop strong relationships with logistics partners, and create robust business continuity plans.
Understanding the pillars is one thing; implementing them is another. Here’s how to make them work together.
Start with Strategic Sourcing: For most organizations, the first step is to gain control internally. Master Spend Analysis and Sourcing to generate savings and build a strong supplier base. This funds and justifies further investment.

Expand with Global Procurement: As you grow globally, layer on the People, Process, Technology, and Supply Chain disciplines to manage the new complexity effectively.
Create Synergies:
The data from your Spend Analysis (Pillar 1 of Sourcing) informs the Technology (Pillar 3 of Global) you need to implement.
Your SRM efforts (Pillar 4 of Sourcing) are the foundation for a resilient Supply Chain (Pillar 4 of Global).
Global Processes (Pillar 2 of Global) ensure your Strategic Sourcing strategies are executed consistently worldwide.
To track your progress, monitor these metrics across both frameworks:
Cost Savings: Percentage of savings achieved against baseline.
Supplier Performance: On-Time Delivery (OTD) and Perfect Order Fulfillment rates.
Process Efficiency: Procurement Cycle Time.
Compliance: Contract Compliance Rate and Maverick Spend percentage.
Innovation: Number of value-add ideas or projects initiated by suppliers.
Q1: What's the real difference between "purchasing" and "procurement"? I hear them used interchangeably.
A: Think of it like this: purchasing is the specific act of buying—the transaction itself. Procurement is the entire process, from identifying a need to paying the invoice. It includes sourcing, negotiation, and contract management. Procurement is the strategy; purchasing is the final tactical step.
Q2: We're an SME with a limited budget. Can we even implement this "four pillars" approach?
A: Absolutely. You don't need a massive budget, just a shift in mindset. Start small. Focus on one pillar, like Spend Analysis. Even just categorizing your last year's expenses in a spreadsheet can reveal huge opportunities. The frameworks are scalable; the key is to be intentional rather than reactive.
Q3: Which pillar should we tackle first if we're starting from zero?
A: It almost always starts with Spend Analysis. You can't build a smart strategy in the dark. Knowing exactly where your money goes is the flashlight that shows you which suppliers to renegotiate with, which categories to consolidate, and where your biggest risks might be hiding.
Q4: How do we get other departments (like Finance or Operations) to buy into this structured approach?
A: Speak their language. Don't talk about "procurement pillars." Talk to Finance about cost savings and compliance. Talk to Operations about supply reliability and quality. Show them how this process solves theirproblems, and they'll become your biggest allies.
Q5: Is this approach only for manufacturing companies buying raw materials?
A: Not at all! The principles are universal. A tech company can use it for software licenses and cloud services. A hospital can use it for medical supplies and equipment. A marketing agency can use it for freelance talent and ad space. Any organization that spends money can benefit.
Q6: What's a common "rookie mistake" when trying to improve procurement?
A: Focusing solely on unit price. This is the classic error. The cheapest product often comes with hidden costs: poor quality, unreliable delivery, terrible service, or high risk. Always evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes these hidden factors.
Q7: How often should we re-evaluate our suppliers and contracts?
A: It's not a "set it and forget it" deal. For critical suppliers, formal reviews should happen at least annually. But you should be monitoring performance (like delivery times) continuously. The market changes, and so should your relationships. Don't wait for a contract to expire to see if you're still getting a good deal.
Q8: We have great relationships with our long-time suppliers. Why should we rock the boat with a formal process?
A: A formal process isn't about replacing trust; it's about building on it. A good contract and regular performance reviews protect both of you. It ensures expectations are clear and reduces the chance of a misunderstanding that could damage that great relationship you've worked hard to build.
Q9: What role does sustainability play in modern procurement?
A: A huge and growing one. It's now a core component of risk management and brand reputation. Companies are increasingly evaluated on their Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) practices. This means assessing suppliers on their ethical labor practices, environmental impact, and carbon footprint, not just cost and quality.
Q10: Can AI and automation really help, or is it just a buzzword?
A: It's real and a game-changer, especially for the first pillar (Spend Analysis). AI can automatically cleanse and categorize thousands of invoices in minutes, uncovering patterns a human would miss. It can also monitor global risks and even predict supplier viability. It frees up your team to focus on strategic work like negotiation and relationship building.
Contact us
Call Us: +86 193 7668 8822
Email:[email protected]
Add: Building B, No.2, He Er Er Road, Dawangshan Community, Shajing Street, Bao'an District, Shenzhen, China